Nov 3, 2023This article will discuss the anatomy of the peritoneum, including key related topics; peritoneal cavity, omenta, mesentery, ligaments, and peritoneal relations. Contents Peritoneum Peritoneal cavity Divisions Lesser sac (omental bursa) Greater sac Mesentery Omentum Peritoneal ligaments Peritoneal relations Clinical relations Ascites Peritonitis
Engineering Organ-on-a-Chip Systems for Vascular Diseases | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
Highlights We’re unable to load Study Guides on this page. Please check your connection and try again. (ID: 26467b7e2dcb410a9fdde5272a34fcd5) Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Demonstrate the anatomical position Describe the human body using directional and regional terms

Source Image: mountelizabeth.com.sg
Download Image
Pain from the visceral peritoneum is referred to areas of skin ( dermatomes) which are supplied by the same sensory ganglia and spinal cord segments as the nerve fibres innervating the viscera. Fig 1 – The structure of the peritoneum and the peritoneal cavity. Note how the visceral layer invaginates to cover the organs. Peritoneal Cavity
Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
Peritoneum Peritoneum. Your peritoneum is a membrane that lines the inside of your abdomen and pelvis (parietal layer). It also covers many of your organs inside (visceral layer). The space in between these layers is called your peritoneal cavity. Folds of tissue form double layers, including your omentum, which hangs down the front of your abdomen, and
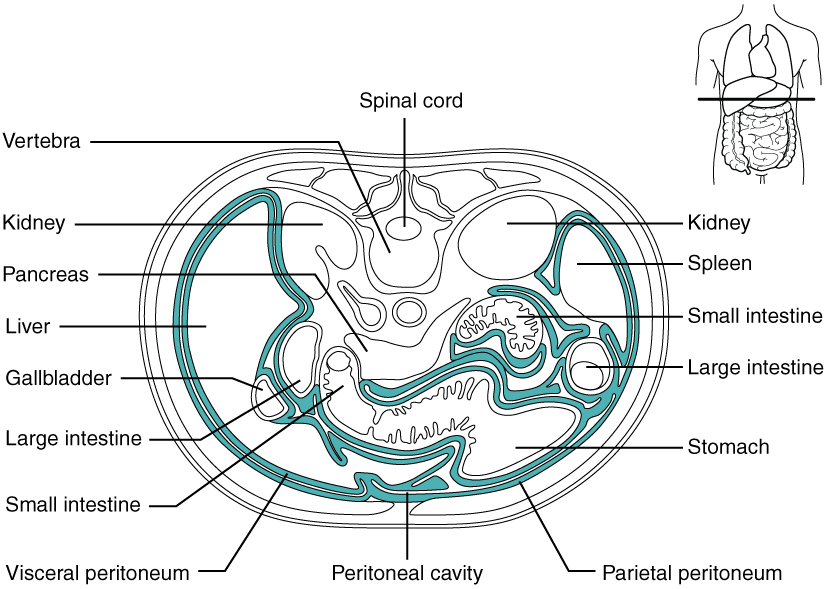
Source Image: anatomytool.org
Download Image
Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Peritoneum.
Peritoneum. Your peritoneum is a membrane that lines the inside of your abdomen and pelvis (parietal layer). It also covers many of your organs inside (visceral layer). The space in between these layers is called your peritoneal cavity. Folds of tissue form double layers, including your omentum, which hangs down the front of your abdomen, and Jul 25, 2023The peritoneum is the serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It is composed of mesothelial cells that are supported by a thin layer of fibrous tissue and is embryologically derived from the mesoderm. The peritoneum serves to support the organs of the abdomen and acts as a conduit for the passage of nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatics. Although the peritoneum is thin, it is made of
OpenStax AnatPhys fig.23.4 – The Peritoneum – English labels | AnatomyTOOL
See Answer Question: Correctly label the following parts of the peritoneum. Correctly label the following parts of the peritoneum. Here’s the best way to solve it. Powered by Chegg AI Share Share Step 1 Identi… View the full answer Step 2 Unlock Unlock Step 3 Unlock Unlock Step 4 Unlock Unlock Step 5 Unlock Unlock Answer Unlock Unlock Premium Photo | The abdominal wall is made up of a set of layered structures that surround and enclose the abdominal cavity

Source Image: freepik.com
Download Image
Appendix | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org See Answer Question: Correctly label the following parts of the peritoneum. Correctly label the following parts of the peritoneum. Here’s the best way to solve it. Powered by Chegg AI Share Share Step 1 Identi… View the full answer Step 2 Unlock Unlock Step 3 Unlock Unlock Step 4 Unlock Unlock Step 5 Unlock Unlock Answer Unlock Unlock

Source Image: radiopaedia.org
Download Image
Engineering Organ-on-a-Chip Systems for Vascular Diseases | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Nov 3, 2023This article will discuss the anatomy of the peritoneum, including key related topics; peritoneal cavity, omenta, mesentery, ligaments, and peritoneal relations. Contents Peritoneum Peritoneal cavity Divisions Lesser sac (omental bursa) Greater sac Mesentery Omentum Peritoneal ligaments Peritoneal relations Clinical relations Ascites Peritonitis

Source Image: ahajournals.org
Download Image
Peritoneum Pain from the visceral peritoneum is referred to areas of skin ( dermatomes) which are supplied by the same sensory ganglia and spinal cord segments as the nerve fibres innervating the viscera. Fig 1 – The structure of the peritoneum and the peritoneal cavity. Note how the visceral layer invaginates to cover the organs. Peritoneal Cavity
Source Image: medicinehack.com
Download Image
A&P II- Exam IV: The Digestive System (Connect) Flashcards | Quizlet Jan 17, 2023The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom. It covers most of the intra-abdominal, or coelomic, organs. It is composed of a layer of mesothelial tissue, supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. The peritoneum provides support and protection for the abdominal organs, and is the main

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
Intraperitoneal Delivery Systems | SpringerLink Peritoneum. Your peritoneum is a membrane that lines the inside of your abdomen and pelvis (parietal layer). It also covers many of your organs inside (visceral layer). The space in between these layers is called your peritoneal cavity. Folds of tissue form double layers, including your omentum, which hangs down the front of your abdomen, and
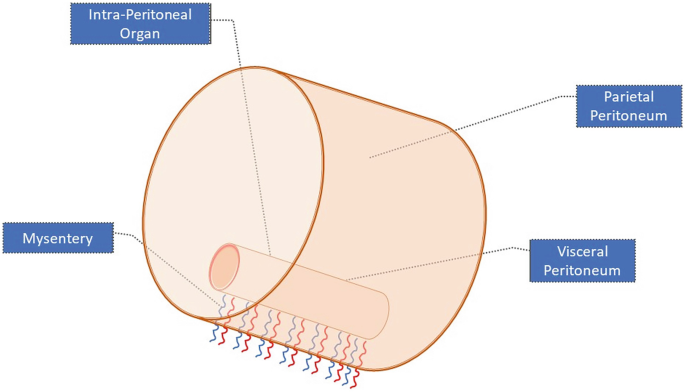
Source Image: link.springer.com
Download Image
Abdominopelvic Cavity | Definition, Regions & Organs – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Jul 25, 2023The peritoneum is the serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It is composed of mesothelial cells that are supported by a thin layer of fibrous tissue and is embryologically derived from the mesoderm. The peritoneum serves to support the organs of the abdomen and acts as a conduit for the passage of nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatics. Although the peritoneum is thin, it is made of

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Appendix | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
Abdominopelvic Cavity | Definition, Regions & Organs – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Highlights We’re unable to load Study Guides on this page. Please check your connection and try again. (ID: 26467b7e2dcb410a9fdde5272a34fcd5) Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Demonstrate the anatomical position Describe the human body using directional and regional terms
Peritoneum Intraperitoneal Delivery Systems | SpringerLink Jan 17, 2023The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom. It covers most of the intra-abdominal, or coelomic, organs. It is composed of a layer of mesothelial tissue, supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. The peritoneum provides support and protection for the abdominal organs, and is the main