Jul 30, 2022With up to 180 liters per day passing through the nephrons of the kidney, it is quite obvious that most of that fluid and its contents must be reabsorbed. That recovery occurs in the PCT, loop of Henle, DCT, and the collecting ducts. Various portions of the nephron differ in their capacity to reabsorb water and specific solutes.
Sites of solute, electrolyte, and acid-base regulation by the renal… | Download Scientific Diagram
Reabsorption of water and some key electrolytes are regulated and can be influenced by hormones. Sodium (Na +) is the most abundant ion and most of it is reabsorbed by active transport and then transported to the peritubular capillaries. Because Na + is actively transported out of the tubule, water follows it to even out the osmotic pressure
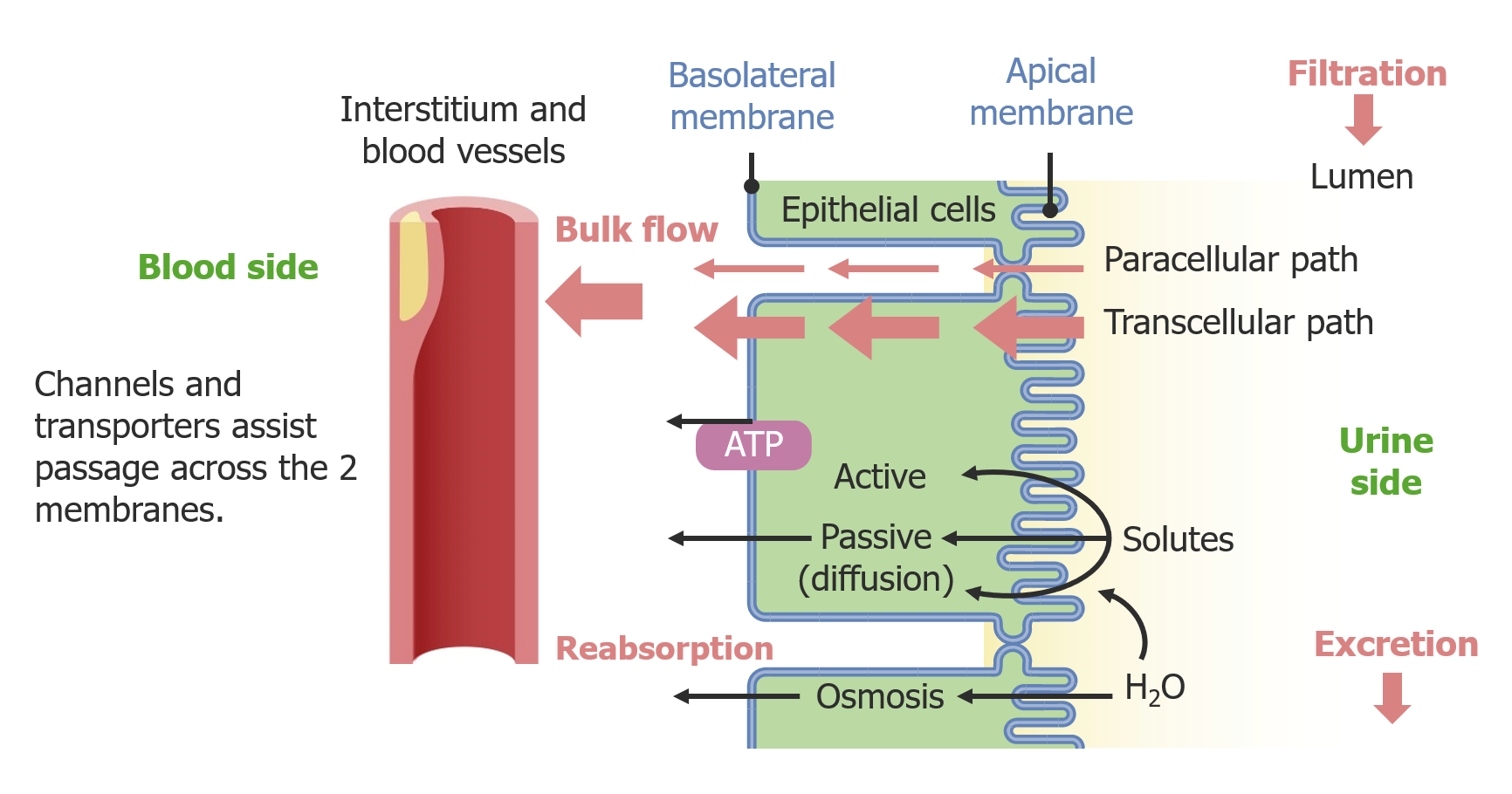
Source Image: lecturio.com
Download Image
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is not associated with the renal corpuscle?, Most electrolyte reabsorption by the renal tubules is ________., Which of the following is the best explanation for why the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) contains so many mitochondria? and more.
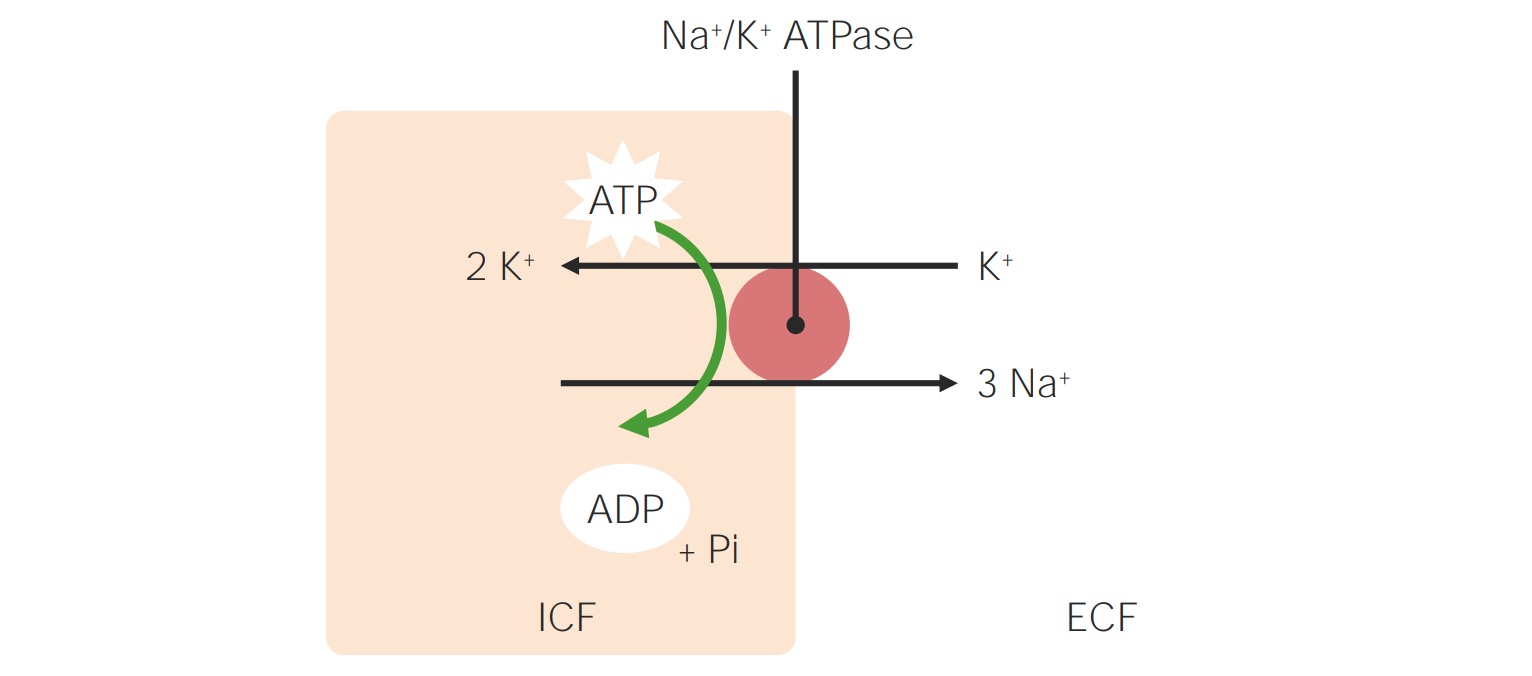
Source Image: lecturio.com
Download Image
Tubular System | Concise Medical Knowledge Renal tubular flow is highly variable owing to the glomerular filtration rate, tubuloglomerular feedback, renal pelvic wall contraction and fluid reabsorption along the nephron. To regulate

Source Image: medicalbiochemist.com
Download Image
Most Electrolyte Reabsorption By The Renal Tubules Is
Renal tubular flow is highly variable owing to the glomerular filtration rate, tubuloglomerular feedback, renal pelvic wall contraction and fluid reabsorption along the nephron. To regulate Accordingly, the renal tubule must absorb most substances filtered at the glomerulus to avoid their loss into urine. However, as indicated above, a small fraction of water and ions that exactly matches the daily input from diet and metabolism must also be excreted.
Tubular Function of Kidney & Electrolyte Balance : MCQ
Tubular Reabsorption of Sodium, Chloride and Fluids. 99% of the glomerular filtrate volume (primary urine, 120 ml/min), 99% of the filtrated sodium and 99% of the filtered Chloride are reabsorbed in the renal tubules of the nephron. The reabsorption is energy consuming process; the needed energy rises linearly with the NaCl-Reabsorption. The Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Pathway Steps, Function, Mechanism, Medication Inhibitors — EZmed

Source Image: ezmedlearning.com
Download Image
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review | Physiology, Human anatomy and physiology, Renal physiology Tubular Reabsorption of Sodium, Chloride and Fluids. 99% of the glomerular filtrate volume (primary urine, 120 ml/min), 99% of the filtrated sodium and 99% of the filtered Chloride are reabsorbed in the renal tubules of the nephron. The reabsorption is energy consuming process; the needed energy rises linearly with the NaCl-Reabsorption.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Sites of solute, electrolyte, and acid-base regulation by the renal… | Download Scientific Diagram Jul 30, 2022With up to 180 liters per day passing through the nephrons of the kidney, it is quite obvious that most of that fluid and its contents must be reabsorbed. That recovery occurs in the PCT, loop of Henle, DCT, and the collecting ducts. Various portions of the nephron differ in their capacity to reabsorb water and specific solutes.

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
Tubular System | Concise Medical Knowledge Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is not associated with the renal corpuscle?, Most electrolyte reabsorption by the renal tubules is ________., Which of the following is the best explanation for why the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) contains so many mitochondria? and more.
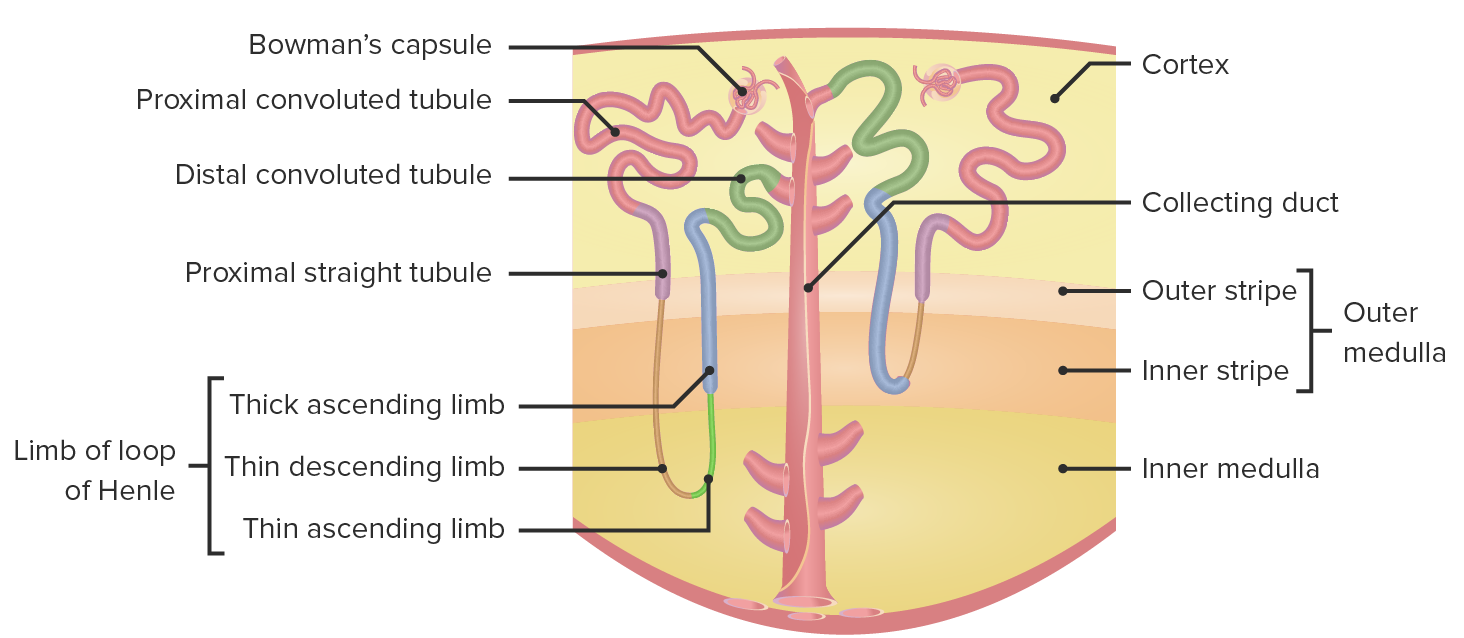
Source Image: lecturio.com
Download Image
My Notes for USMLE — THE NEPRHON EDIT Please note that there´s a… Aug 18, 2023Summary. are the functional units of the kidneys. They are composed of a renal corpuscle (the. ). The main functions of. . Urine production involves filtration of the plasma in the renal corpuscle (a passive process), the secretion of substances to be eliminated (e.g., ) within the renal tubules.

Source Image: mynotes4usmle.tumblr.com
Download Image
Renal Physiology – Glomerular Filtration, Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Renal tubular flow is highly variable owing to the glomerular filtration rate, tubuloglomerular feedback, renal pelvic wall contraction and fluid reabsorption along the nephron. To regulate

Source Image: student-nurse-life.com
Download Image
Osmotic Regulation and Excretion | PDF | Kidney | Endocrine System Accordingly, the renal tubule must absorb most substances filtered at the glomerulus to avoid their loss into urine. However, as indicated above, a small fraction of water and ions that exactly matches the daily input from diet and metabolism must also be excreted.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review | Physiology, Human anatomy and physiology, Renal physiology
Osmotic Regulation and Excretion | PDF | Kidney | Endocrine System Reabsorption of water and some key electrolytes are regulated and can be influenced by hormones. Sodium (Na +) is the most abundant ion and most of it is reabsorbed by active transport and then transported to the peritubular capillaries. Because Na + is actively transported out of the tubule, water follows it to even out the osmotic pressure
Tubular System | Concise Medical Knowledge Renal Physiology – Glomerular Filtration, Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Aug 18, 2023Summary. are the functional units of the kidneys. They are composed of a renal corpuscle (the. ). The main functions of. . Urine production involves filtration of the plasma in the renal corpuscle (a passive process), the secretion of substances to be eliminated (e.g., ) within the renal tubules.